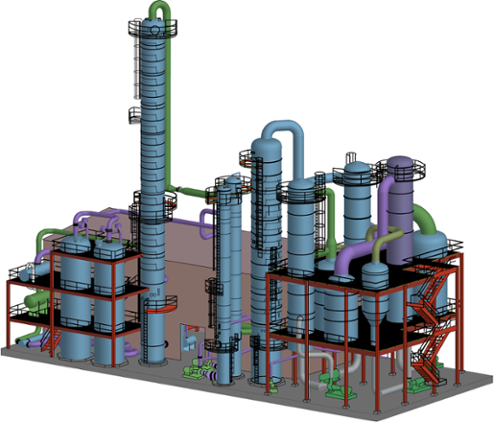
Understanding the Components of a Fuel Ethanol Plant
Comments Off on Understanding the Components of a Fuel Ethanol PlantEnvironmentally conscious consumers demand greener products. This has driven increased interests in a wide variety of sustainable alternatives to products we use every day. Green vehicles – such as hybrids or alternative fuel vehicles – represent some of the most visible alternatives this trend has produced to date. The rise of green vehicles has by association made ethanol fuel increasingly popular.
The increased demand for sustainable fuels has intensified the focus on ethanol fuel production and how the process can be made more energy efficient. Like any fuel refining process, the production of ethanol is quite complex. An alcoholic fermentation broth – typically created in the United States using grain or corn – is repeatedly distilled until it reaches 95 percent of the weight of ethanol. A mixture physically incapable of further distillation is known as an azeotrope, and this azeotrope continues on through processing to extract the ethanol.
Engineered Components for a Complex Process
Careful thought must be given when designing facilities to support the complex process of ethanol production. Several specialized components comprise a fuel ethanol plant as follows:
- Beer/Rectification Columns – First and second stages of water removal
- Molecular Sieve Units – Final stage of water separation
- Evaporation System – Concentrates the thin stillage
Thermal Kinetics is dedicated to providing high quality engineering support to the ethanol production industry. This has only been a broad overview of a selection of the complex components that comprise a Fuel Ethanol Plant. To learn more about these various components, please explore our Interactive Fuel Ethanol Plant today.
Common Uses and Applications for Evaporators
Comments Off on Common Uses and Applications for EvaporatorsAs the name suggests, evaporators are devices that cause a material to evaporate, or enter its gaseous state. Because of their broad range of practical uses, they can be found in a variety of applications, ranging from agriculture to waste management. To illustrate the versatility of these essential devices, we’ll briefly walk you through some of their most common uses and applications below.
Common Uses for Evaporators
 Evaporators are widely employed in most industries that depend on a constant supply of fluids or chemicals. HVAC systems, for example, use evaporator coils to vaporize compressed cooling chemicals, removing heat in the process. These systems also use condenser coils to exhaust the heat outside, making the entire process much more effective.
Evaporators are widely employed in most industries that depend on a constant supply of fluids or chemicals. HVAC systems, for example, use evaporator coils to vaporize compressed cooling chemicals, removing heat in the process. These systems also use condenser coils to exhaust the heat outside, making the entire process much more effective.
Heat recovery evaporators are used to convert seawater into clean water in desalination plants. Utility companies tend to prefer these evaporators over alternative solutions because of their simplicity and minimal energy requirements. The end result is lower operational costs.
Evaporators are also used in oil fields to separate water and various other compounds from crude oil. Though more difficult to use than other types of evaporators, these are nevertheless popular among energy companies because they can reduce operating costs while meeting government-mandated standards. Because they are relatively compact, they can also be easily transported to other locations.
The food industry employs evaporators to achieve product consistency. Coffee is a case in point. Evaporation is also used to concentrate liquid foods such as noodles and make condensed milk, the product of a process that removes water from milk. Similarly, pharmaceutical companies use evaporators to remove excess moisture from drugs, thus improving product stability.
Common Applications for Evaporators
Because of their efficiency, evaporators are well-suited to an array of industrial applications. They are particularly common in processing industries. Food and dairy products such as tomato purees, milk, herbal extracts, gelatin, coconut water, and whey and milk proteins are all processed with the help of evaporators. The same is true for chemicals such as dyes, ammonium nitrate, glycerin, sodium nitrate, paints, and pigments.
Evaporators are also ideal for very low temperature applications in the food and pharmaceutical industries. These include the production of plasma, fermented products, coffee extracts, fruit juices, bulk drugs, glycerin, sweet water, yeast extract, and protein hydrolysate. Whey, gelatin, malt extracts, glucose, fructose, dextrose, sorbitol, and maltodextrin are all produced with evaporators, as well.
Another field in which evaporators are widely used is waste management. Waste management providers rely on them to treat effluents, or wastewater, from various plants, including distilleries, grain mills, abattoirs, textile plants, chemical reactors, and storage tanks.
Designed to serve a variety of practical uses, evaporators are a versatile solution to many common industrial challenges. At Thermal Kinetics, we use our experience and expertise to manufacture evaporators that thrive in any application.
Thermal Kinetics works with companies of every size to develop an evaporator that suits their particular needs. Our wide range of products includes falling film tubular evaporators, rising film tubular evaporators, internal pump forced circulation evaporators, caustic and other specialized concentration systems, forced circulation evaporators, and plate stripping and evaporation systems.
Regardless of your needs, Thermal Kinetics can supply you with an industrial grade evaporator that minimizes operating costs without undermining productivity. Contact us to learn more about how we can help you find the perfect evaporator for your company.